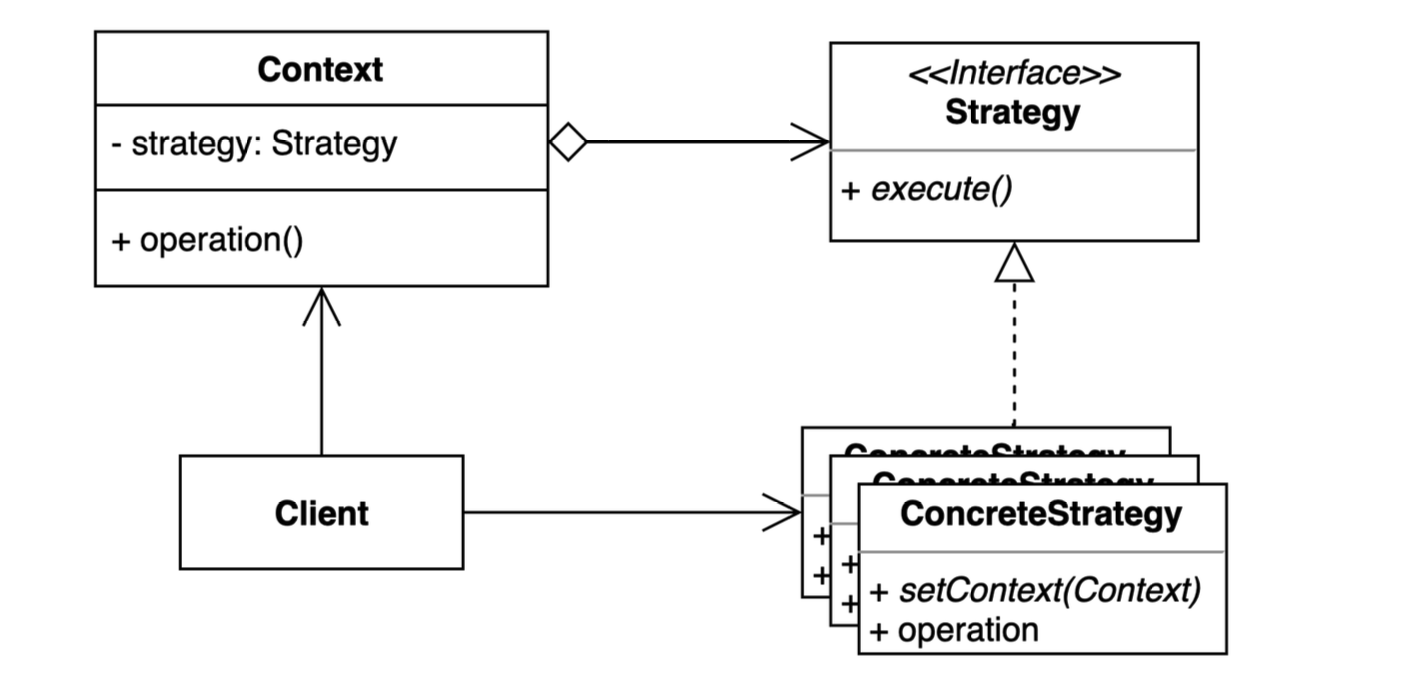
Strategy Pattern
전략 패턴 (Strategy Pattern)
다양한 알고리듬을 캡슐화해 런타임에 교체할 수 있도록 하는 패턴이다.
이 패턴을 사용하면 알고리즘을 사용하는 클라이언트 코드와 알고리즘 자체를 분리할 수 있어 코드의 유연성과 확장성이 높아진다.
패턴 구조
- Strategy : 공통 알고리즘을 정의하는 인터페이스
- ConcreteStrategy : Strategy 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스이다. 실제 알고리즘을 구현한다.
- Context: 전략 객체를 필요한 시점에 실행하는 역할을 한다.
패턴 적용 전
예를 들어 쇼핑몰에서 할인을 적용하는 코드를 작성해보자. 할인은 할인율을 적용하는 방식과 할인 금액을 적용하는 방식이 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
enum class DiscountType {
PERCENT, PRICE
}
class Product(val price: Int) {
fun getDiscountedPrice(discountType: DiscountType, amount: Int): Int {
return when(discountType) {
DiscountType.PRICE -> price - amount
DiscountType.PERCENT -> price - (price * amount / 100)
else -> price
}
}
}
이 후 신규 고객 할인이라는 할인 방식이 추가되었다고 가정해보자
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
enum class DiscountType {
PERCENT, PRICE,
NEW_CUSTOMER // 신규 고객 할인
}
class Product(val name: String, val price: Int) {
fun getDiscountedPrice(discountType: DiscountType, disCountAmount: Int = 0): Int {
return when (discountType) {
DiscountType.PRICE -> price - disCountAmount
DiscountType.PERCENT -> price - (price * disCountAmount / 100)
DiscountType.NEW_CUSTOMER -> price - 1000 // 신규 고객 할인
else -> price
}
}
}
이 코드의 문제는 할인 방식이 추가될 때마다 Product 클래스의 getDiscountedPrice 메소드를 수정해야 한다는 것이고 이는 OCP를 위반한다.
애초에 Product 클래스가 할인 방식에 대한 구체적인 구현을 알고 있어야 한다. 즉, 책임이 너무 많다.
패턴 적용 후
먼저 할인 Strategy 인터페이스를 정의한다. 이 인터페이스는 할인 계산을 위한 메서드를 정의한다.
1
2
3
interface DiscountStrategy {
fun applyDiscount(price: Int, amount: Int): Int
}
이 후 구체적인 할인 전략 클래스를 구현한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class PriceDiscountStrategy : DiscountStrategy {
override fun applyDiscount(price: Int, amount: Int): Int {
return price - amount
}
}
class PercentDiscountStrategy : DiscountStrategy {
override fun applyDiscount(price: Int, amount: Int): Int {
return price - (price * amount / 100)
}
}
class NewCustomerDiscountStrategy : DiscountStrategy {
override fun applyDiscount(price: Int, amount: Int): Int {
return price - 1000
}
}
이 후 Product 클래스는 할인 전략을 주입받아 할인을 적용할 수 있도록 변경한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class Product(val price: Int) {
fun getDiscountedPrice(discountStrategy: DiscountStrategy, amount: Int): Int {
return discountStrategy.applyDiscount(price, amount)
}
}
이제 클라이언트 코드에서는 할인 전략을 주입하여 사용할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
fun main() {
val product = Product(10000)
val priceDiscountStrategy = PriceDiscountStrategy()
val percentDiscountStrategy = PercentDiscountStrategy()
val newCustomerDiscountStrategy = NewCustomerDiscountStrategy()
println(product.getDiscountedPrice(priceDiscountStrategy, 1000))
println(product.getDiscountedPrice(percentDiscountStrategy, 10))
println(product.getDiscountedPrice(newCustomerDiscountStrategy, 0))
}
장단점
장점
- 런타임에 알고리즘을 쉽게 교체할 수 있다.
- 기존 코드를 수정하지 않고도 새로운 전략을 추가할 수 있다.
- 상태에 따른 동작을 분리함으로써 코드의 가독성이 높아진다.
- 관심사를 분리하기 때문에 유지보수에도 좋고 테스트하기도 용이해진다.
단점
- 복잡도가 증가한다.
- 많은 클래스가 생성되어 관리가 어려워질 수 있다.
Reference
- 코딩으로 학습하는 GoF의 디자인 패턴 - 백기선
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.